In the process of global 5G commercialization, private networks are considered to be a form of service that can compete with the public network. With the development of 5G applications, the industry’s voice for private networks is getting higher and higher, although the current 5G construction is still based on public networks. Mainly, but the industrial ecology of private networks has quietly grown. Nokia, Ericsson, Huawei take the lead
Recently, the Global Mobile Suppliers Association (GSA) announced the establishment of a ” GSA Private Mobile Networks Special Interest Group (SIG) “, which aims to unite leading mobile communication enterprises to jointly track and promote the development of the private mobile network ecosystem. A highlight of this special interest group is that its founding members are the three telecom equipment vendors Nokia, Ericsson and Huawei.
In the process of global 5G commercialization, private networks are considered to be a form of service that can compete with the public network. With the development of 5G applications, the industry’s voice for private networks is getting higher and higher, although the current 5G construction is still based on public networks. Mainly, but the industrial ecology of private networks has quietly grown.
Rapid growth of private networks
In addition to the founding members Nokia, Ericsson and Huawei, this special interest group also includes Mavenir, Keysight and Private 5G and LTE as permanent members. GSA said that in the coming months, more leading manufacturers will be announced as members of this special interest group. The goal of this SIG is to define the ecosystem, track it, and facilitate its continued development to support industry outreach.
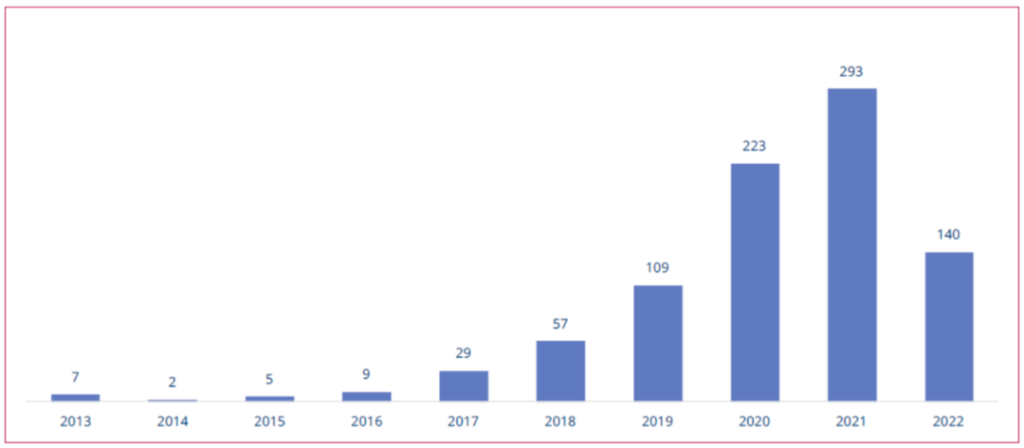
The Private Mobile Networks Special Interest Group was established against the background of the rapid growth of private mobile networks in recent years. According to the latest tracking report released by GSA in August this year, as of the end of June 2020, at least 889 organizations around the world had deployed LTE private networks or 5G private networks, and 140 private networks had been deployed in the first half of this year.

According to GSA tracking data, before 2017, the number of new customers in private networks was only single digits each year. Since 2017, the deployment of private networks has accelerated, and nearly 300 new customers have deployed private networks in 2021.
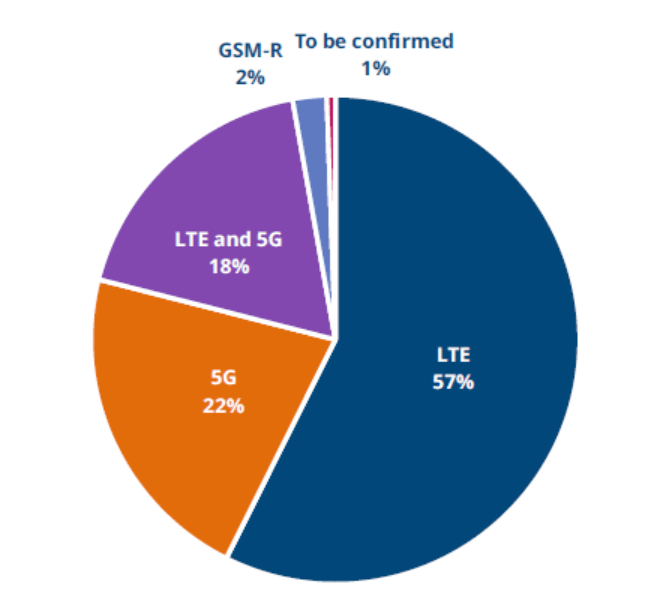
Private networks are currently dominated by LTE and 5G, and according to the GSA report, LTE technology accounts for the majority of these deployments. Of all private networks, 57% were deployed using LTE technology, 5G accounted for 22%, and LTE and 5G dual-mode deployments accounted for 18%. The author predicts that with the maturity of 5G technology, private networks deployed with 5G will gradually become mainstream.
The acceleration of private network deployment is supported by the rapid growth of demand in various industries. Rising demands for data, security, digitization and enterprise mobility in modern commercial and government agencies are driving the need for 4G LTE-based and, increasingly, 5G-based mobile private networks, GSA analysis, and these types of organizations They are combining network systems with technologies such as artificial intelligence and big data to transform operations, improve automation and efficiency, or provide new services.
In the GSA tracking data, the manufacturing industry is the industry that deploys the most private networks. Currently, 165 customers have deployed commercial networks. By the end of 2021, the number will be 111 customers; followed by the education industry, 95 customers have deployed commercial networks. Networks, third and fourth are mining and power utilities, with 71 and 64 commercial networks deployed, respectively.
Globally, these organizations deploying LTE or 5G private networks are located in 70 countries and regions around the world, with the United States leading the way, followed by Germany, China, the United Kingdom and Japan. According to GSA executives, “Mobile private networks are a microcosm of the wider 4G and 5G ecosystem. There is a strong positive correlation between spectrum liberalization and the adoption of mobile private networks.” We can see that in recent years Germany , Japan, France, the United States and other countries have released a large amount of radio spectrum for enterprises, which has accelerated the deployment of private networks in these countries.
It is worth mentioning that the private mobile networks tracked by GSA mainly focus on 4G/5G mobile networks based on 3GPP, and these networks are only used by private entities such as enterprises, industries or governments, are not open to the public, and use 3GPP definitions. spectrum. Therefore, these private networks do not include networks based on other standards, including technologies such as Wi-Fi, Tetra, WiMAX, Sigfox, and LoRa, nor do they include network slicing of public networks or virtual network functions on routers, or operators in enterprises. Deploy additional sites near the location.
The large-scale benefits of 3GPP-based private networks in the future will attract various entities. IDC research predicts that worldwide private LTE/5G infrastructure revenue will reach $8.3 billion by 2026, a significant increase from $1.7 billion in 2021, and is expected to achieve an annual growth rate of 35.7% during the 2022-2026 forecast period compound annual growth rate.
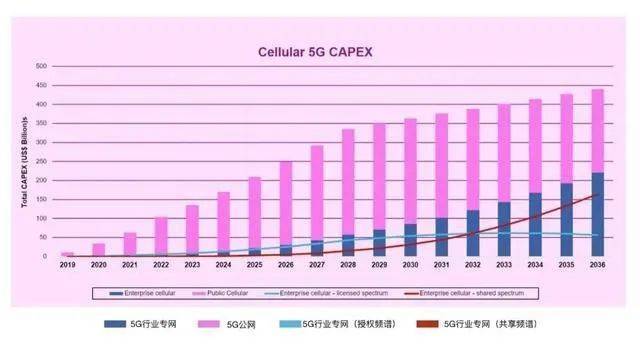
A previous report from ABI Research showed that global spending on 5G private networks will exceed 5G public networks by 2036, a prediction that seems more aggressive.
According to the forecast of ABI Research, by 2026, the capital expenditure of cellular wireless private network will exceed 200 billion US dollars. In the face of this big cake, I believe that telecom equipment manufacturers will not be unmoved.
Equipment vendors are expected to become the first major force in private networks
This time, Nokia, Ericsson and Huawei, as founding members, jointly launched the GSA Private Mobile Network Special Interest Group, which reflects the high importance that telecom equipment manufacturers attach to private networks. Due to the potential market and benefits of private networks in the future, many players have entered the field, and telecom equipment manufacturers are expected to become the first major force in these groups.
Telecom operators are undoubtedly powerful players in the private network ecosystem. Due to long-term operation of public networks and numerous enterprise customers, telecom operators have rich experience in all aspects of end-to-end cellular networks, and their positions in the communications industry can promote the implementation of a large number of private networks. In the 5G era, operators are of course unwilling to give up the enterprise private network market. For example, European operator Vodafone has launched RedBox, an integrated 5G product for enterprise private networks, Telefonica provides 5G private network services for Mercedes-Benz factories, and Verizon goes abroad to deploy 5G private networks for British ports. Of course, limited by the flexibility of institutional mechanisms and frequencies, operators still have many difficulties in providing customers with independent private networks.
Internet companies, especially cloud computing giants, have become a major force in private networks . Typical vendors include AWS, Microsoft, and Google. For example, AWS launched its enterprise 5G private network solution, AWS Private 5G, at the end of last year. This is a new AWS managed service designed to allow enterprises to easily build their own 5G private network. AWS claims that AWS Private 5G allows enterprises to procure, deploy and expand 5G private networks in days instead of months, posing challenges to 5G public networks. In June of this year, Google officially launched its cellular wireless private network solution for enterprises, which is based on its “Google Distributed Cloud Edge” product released last year and will leverage Google’s ISV ecosystem, Address the unique performance, service levels and economic needs of key verticals by combining private network capabilities with a complete edge computing application stack.
The entry of Internet companies has sounded the alarm for telecommunications equipment manufacturers. Public cloud manufacturers represented by Internet giants have entered the cellular wireless private network market, breaking the pattern that this field is dominated by professional telecommunications equipment manufacturers, and has invaded to a large extent. The “exclusive” territory of the telecommunications industry, earning the benefits of traditional telecommunications manufacturers, and causing huge pressure on traditional telecommunications manufacturers. Therefore, telecom equipment manufacturers will also launch a “counterattack” in this field.
For a long time, telecom equipment vendors have also been the main force of private networks, with specialized private network products and solutions. Take Nokia as an example. In recent years, the manufacturer has focused its strategy on the enterprise private network market and launched two 5G private network solutions, Nokia Digital Automation Cloud (DAC) and Modular Private Wireless (MPW). As early as 2019, Nokia announced that it had signed wireless private network agreements with more than 120 companies, covering multiple industries and fields such as transportation, energy, public sector, logistics and manufacturing, and provided overall private network solutions through its DAC platform.
In the author’s opinion, as the core participants of mobile communications, telecom equipment vendors such as Nokia, Ericsson, and Huawei have obvious advantages in the field of enterprise private networks.
First of all, equipment manufacturers have the advantages of technology and standards . Private mobile networks are based on 3GPP technologies and standards, and telecom equipment vendors are the core participants in the 3GPP camp, and they have a large number of technologies and standards that need to be accumulated over a long period of time. The “Global 5G Patent Activity Report (2022)” released by the Chinese Academy of Communications shows that among the industry entities declared by 5G patents, Huawei ranks first, accounting for 14% of the global patent family, while ZTE, Nokia, Ericsson and other telecom equipment manufacturers Its patent accumulation is in the top 10, which reflects the deep accumulation of equipment manufacturers in the long-term research and development of communication technology.
Secondly, the product capabilities of equipment manufacturers have absolute advantages. Telecom equipment manufacturers have decades of R&D and production history of telecom equipment products and have gone through many iterations. Compared with operators and Internet manufacturers, they have irreplaceable advantages in this regard. Although in recent years, with the development of Open RAN, manufacturers in this field have also entered the 5G private network market, but Open RAN is far into dedicated equipment in terms of performance and stability, and it is difficult to challenge the status of traditional telecom equipment manufacturers in the short term.
Once again, equipment manufacturers have rich experience in network deployment . Although telecom operators are the main body in the construction and operation of communication networks, equipment manufacturers are involved in the whole process of construction and operation, and jointly solve a large number of problems in construction and operation. After these experiences, telecom equipment vendors also have rich experience in the deployment and operation of private networks, especially for Internet companies, they have obvious advantages in this regard.
Finally, equipment manufacturers have a large number of enterprise users. In the past decades of operation, enterprise customers have always been an important customer group for telecom equipment manufacturers. The equipment manufacturers have dedicated enterprise customer departments and have invested a lot of resources to serve the digitalization of enterprises. This lays the foundation for providing private networking solutions to enterprises.
Prior to this, Huawei had not made much clear statement on private networks, especially 5G private networks. This time, as a founding member, we jointly launched the GSA Private Mobile Network Special Interest Group, which can be said to be an obvious statement on 5G private networks. , as well as the continued layout in this field reflects.
The 5G private network ecosystem has gradually formed, and there are more participants in this field, which will present a new supplier landscape. The efforts of telecom equipment manufacturers will form an advantage among these entities and are expected to become the first main force of private network providers
Read more updates on www.qfiles.org
